A to Z List of Marketing Terms for Libraries

The Graphical A to Z List of Marketing Terms and Tools Every Librarian Should Know

Isn’t it frustrating as a librarian or info pro working hard to promote your library’s services and programs and you come across marketing advice with ideas or terms that are unfamiliar? It’s annoying that marketing has a language all its own with enough jargon to fill sizeable dictionaries and leave non-experts scratching their heads. You just want to get your work done!
Add to that, we have our own library terms and we barely had time in our LIS programs or on the job to learn all of THOSE and now we add the foreign language of marketing too?!
I’m here to translate a lot of those foreign marketing terms. I have the unique skill of being trained to speak both ‘marketing-ese’ and ‘library land lingo’.
Now, there are plenty of good glossaries and dictionaries already online to explain various marketing terms and I’ve included some of them in the additional resources at the end. But … they are all geared towards big businesses, for-profits, those who already know about marketing, and they are missing examples and illustrations of the concepts at work.
So I created this illustrated, annotated, A to Z guide to the marketing terms all librarians and info pros should know about – and we were never taught in library school.

Marketing Terms Glossary for Libraries, Nonprofits, New Marketers
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A Terms
Above the Fold – term refers back to days of print newspapers where the primary or leading story was positioned above the horizontal fold across the newspaper – this was prime placement because of how newspapers were stacked and delivered and guaranteed it was the first item seen; in web terms, it means copy or images that appear on a page before the user needs to scroll Automation – tools, usually software, that help you with streamlining tactics, workflows and measurement of marketing, to save time and money; automation tools are often behavior-based to trigger other actions , instead of you manually sending emails one-by-one after you learn of an action or intent. Many marketing automation systems deal heavily with email marketing, but others incorporate social media and other website actions. Automation is also about the planning and strategy of designing marketing workflows so that they CAN be automated to degrees. Automation tools are often directed at large or enterprise companies with larger budgets.
Automation – tools, usually software, that help you with streamlining tactics, workflows and measurement of marketing, to save time and money; automation tools are often behavior-based to trigger other actions , instead of you manually sending emails one-by-one after you learn of an action or intent. Many marketing automation systems deal heavily with email marketing, but others incorporate social media and other website actions. Automation is also about the planning and strategy of designing marketing workflows so that they CAN be automated to degrees. Automation tools are often directed at large or enterprise companies with larger budgets.
 e.g. your system automatically sends emails based on certain activity on certain pages of your website, or the system automatically sends one set of email messages to new list subscribers, another set to those who read a certain ebook, and another set to those who purchased a particular product.
e.g. your system automatically sends emails based on certain activity on certain pages of your website, or the system automatically sends one set of email messages to new list subscribers, another set to those who read a certain ebook, and another set to those who purchased a particular product.
Automation tools/software: Pardot, Silverpop, Marketo, Act-on, HubSpot
Autoresponder – part of an email service that allows you to send out pre-scheduled messages to your email list, often in a series of emails. You decide the order and the frequency, they send automatically based on a trigger (e.g. signing up for your email list triggers 1st email at day 1, another a week later, a third a week after that – no matter when someone signs up). Autoresponders are usually a paid feature of an email marketing service.
Awareness – the degree to which a person can easily recognize and identify (unprompted) an organization or brand and link it to the products or services it offers, to its marketing campaigns and/or to its tagline or slogan; sometimes referred to as ‘top of mind awareness’, or ‘brand awareness.’
B Terms
B2B (Business-to-Business) – used to describe marketing for products and services whose main customers are other businesses. E.g. Oracle and Cisco sell their products to corporations, not individuals; Comcast and American Express have products they sell to consumers and ones they sell to businesses, each with different campaigns and messages. B2B marketing may use the same tools and tactics as those directly to individual consumers.
B2C (Business to Consumer) – used to describe marketing campaigns that promote products or services directly to individual consumers. Your local plumber, Target, Nike, and McDonald’s are all B2C marketers.
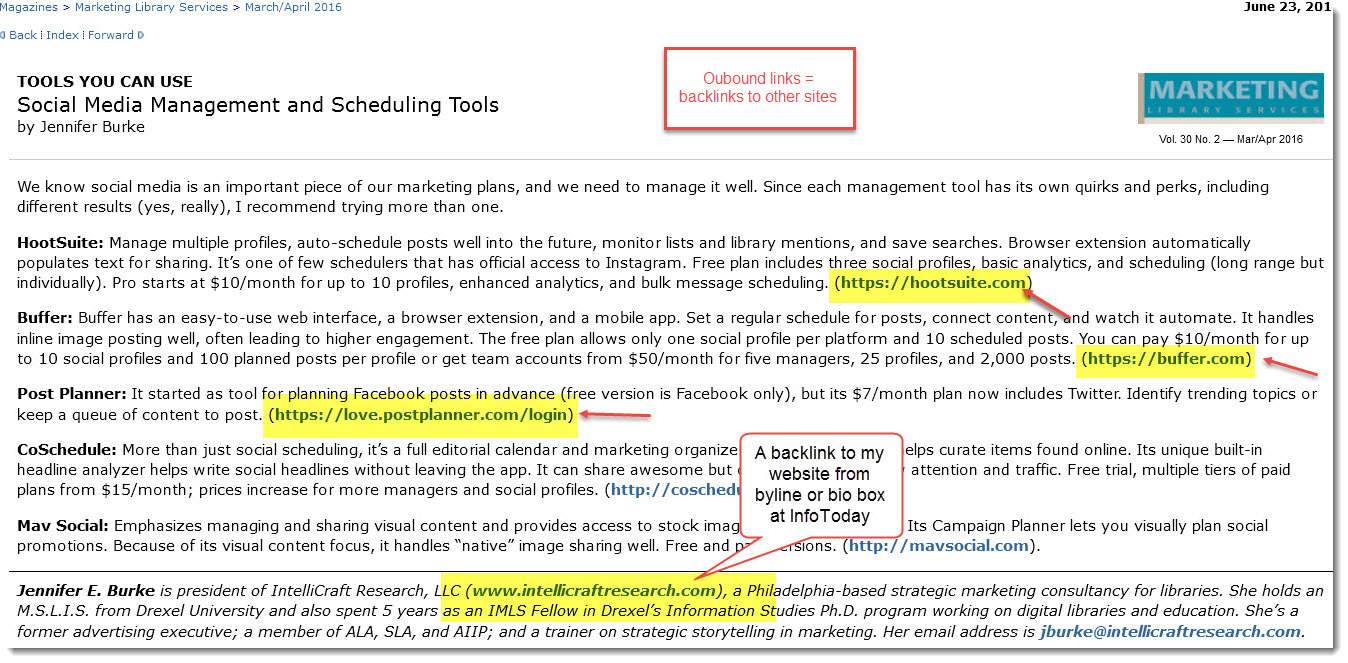
Backlinks – incoming links to your website from another website; backlinks are still considered important in SEO, but only if coming from high quality sites; also called ‘inbound links’
Benchmarking – a point of reference comparison or measurement on some set of standards or metrics, often used versus similar organizations to yours
Body copy – the main text in a piece of content, which provides details, benefits, features or other necessary information; more detailed and longer than headlines or subheads. Can refer to text in a blog post, in a paid ad, in a flyer or any other text-based marketing piece.
Bounce Rate – percent of visitors to your website/page who navigate away from that page after viewing only that page (you want as low a bounce rate as you can get)
B-Roll – film or video footage that is not part of the original or main script or shooting plan or doesn’t feature whomever is talking on-camera; often used to give context, sense of place or surroundings, actions, crowds or visual information while a narrator or voice-over gives additional info; b-rolls ‘shows, not tells’.
Byline – the ‘about the author’ information, often at the end of an article or blog post – especially on sites other than your own. Contains a link back to your website or a call-to-action link for readers. Also called a ‘bio box’, ‘author box’ or ‘resource box’.
C Terms
Call To Action (CTA) – each marketing piece should have some kind of CTA – asking the reader to do something. You could invite them to sign up for your email newsletter, to go to page to donate to your nonprofit campaign, click a link for a product or service you use and recommend [use your Amazon Affiliate link], use the button for your online appointment scheduler or click a link to buy something. The point of marketing is to inspire action – so content should have directions on what action to take.
E.g. “call now”, “view now”, “buy now”, “follow me”, “sign up here”, “learn more now”, “download this”, “sign up to participate”, “donate now”, “sign up here for free webinar”, “get your free card now”, “speak out”, “join us now”, “Volunteer today”
Case Study – for content marketing context, share the story of one of your clients, customers, patrons or reader of your blog. Tell about their experience using your services, programs or advice.
Channel – can refer to types of media, e.g. TV, print, radio, internet, social media and even the specific platforms or sources themselves; or could mean the method or manner of distributing goods, products – linking a producer to end customer.
Click-through-Rate (CTR) – the number of people who clicked a link vs. who just saw the link and took no action. Commonly used as a metric for email marketing (% clicked link in email = signal of real engagement), or for an online ad (% who clicked on ad vs. saw ad). Clicks ÷ Impressions = CTR [if 100 people see the link and 10 click it, your CTR = 10%]
Collateral – the printed (sometimes means electronic) information used to explain or give background on a company or organization and to help a person buy a product or service or make a donation; e.g. brochures, information sheets, rack cards, business cards, print (or email) newsletters, fact sheets, press kits, media kits, staff or team member biographies, websites, and annual reports
Org Fact sheet – to help employees, key  stakeholders or media members to learn important facts about organization at quick glance; inc founding or history information, key dates, location(s), images of key buildings or facilities, names and brief background of key staff, founders, historical figures in organizational history, key photos, contact info; usually all on 1 attractively designed page, ready to hand/send out or download as PDF
stakeholders or media members to learn important facts about organization at quick glance; inc founding or history information, key dates, location(s), images of key buildings or facilities, names and brief background of key staff, founders, historical figures in organizational history, key photos, contact info; usually all on 1 attractively designed page, ready to hand/send out or download as PDF
Product/Service Fact sheet – keep one for each key service or major product; inc function or value, key benefits to users/customers, distinctive features that set it apart, comparison to similar products/services, statement on quality or reliability, pricing, and/or availability
Press/Media Kit – all the information a reporter or media member needs to know about your organization at a glance; they can be collected in 1 place or page on your website, available to download, or printed physically and sent on request or handed out at events; Inc: logo and appropriate way to display it; company/org fact sheet, key product/service fact sheet(s), copy of recent articles or press mentions of your org; a current press release; card or contact information
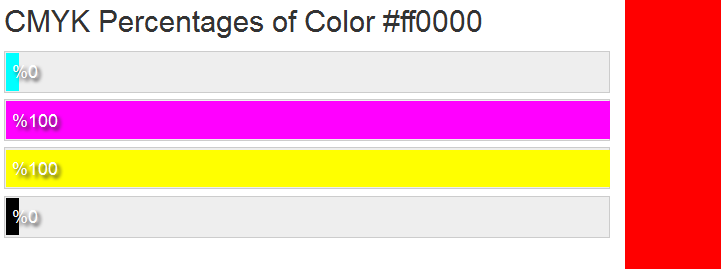
Color Codes – also known as ‘color models’; because we need more precise ways to consistently represent and display the same color in web and printed materials, each color has a set of codes (and because ‘blue’ could be anything between ‘sky’, ‘ocean’ or ‘denim’); if you are getting material printed, you may be asked for CMYK, if it’s purely on the web, use RGB or Hex. Nifty site to find hex codes for all variations of a color (0to255.com), find or translate codes across models (color-hex.com), select color palettes (Coolors)
CMYK – ‘process color’ – representing the 4 colors in physical printing ink, Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key (Black) – for paint, pigment, inks where you add various % of colors and if you keep adding you’d eventually get black (but in practice it comes out muddy, hence the use of the forth color, K (pure black).
e.g Black = 0.00, 0.00, 0.00, 1.00 Red = 0.00, 1.00, 1.00, 0.00 Magenta = 0.00, 1.00, 0.00, 0.00
RGB – a projected light color system; represents colors with 3 separate numbers from 0 to 255, one number each to represent R(red), G(green) and B(blue) values that make up a color; most computer devices and screen use RGB colors
e.g. Black = (0, 0, 0) Red = (255, 0, 0) magenta (255, 0, 255)
 Hex Codes (hexadecimal) – computer friendly, 6-character alpha-numeric combination beginning with # to also represent the spectrum of values of Red, Green and Blue; hex codes are used in ‘legacy’ HTML and CSS;
Hex Codes (hexadecimal) – computer friendly, 6-character alpha-numeric combination beginning with # to also represent the spectrum of values of Red, Green and Blue; hex codes are used in ‘legacy’ HTML and CSS;
e.g. Black = #000000 Red = #FF0000 Magenta = #ff00ff
 Content – any piece of information you share with readers – for instructional, educational, entertainment or persuasive purposes. It can be long or short, text or visual, audio, video, etc. Blog posts, white papers, slide shows, videos, podcasts, short ebooks, social media posts and infographics are all types or formats of content.
Content – any piece of information you share with readers – for instructional, educational, entertainment or persuasive purposes. It can be long or short, text or visual, audio, video, etc. Blog posts, white papers, slide shows, videos, podcasts, short ebooks, social media posts and infographics are all types or formats of content.
Content Management System – a web application or framework that allows users to easily develop, add, edit, and manage website content via a common user interface and can support multiple users working in the same system, collaboratively (files, media, articles, other digital content). E.g. Drupal, Joomla, WordPress, Wikis, Moodle, Rainmaker etc.
Conversion – someone taking a desired action (doesn’t always refer to a customer or a purchase); actions could include: subscribing to an email, download something, donate, sign up for event, watch video, send follow-up contact form, initiate chat, send email, etc
Conversion Rate – the number of visitors/users/leads who ‘convert’ into or through a desired action out of the total number of visitors/users/leads who visited a web page, saw an ad, visited a landing page, etc. Example – how many visitors filled out an email opt-in form vs. the number who visited the page (or clicked the link to open the opt-in). Tip: Conversion rates tend to be low (<10% is common) but can vary and increase depending on factors like what’s being offered, good headlines, emotional appeals, clear benefits, social proof or on-page graphics.
Copywriting – writing in order to promote something and inspire action – for a business, organization, nonprofit, person, opinion or idea. Copywriting’s goal is persuasion, through compelling, engaging, targeted writing.
Copy – text or writing, usually for marketing purpose; can be headline copy, body copy, footer copy, disclaimer copy, policy copy, sales copy, etc
Cost Per Action (CPA) – an online advertising model where the person/org buying pays only for the specified action (i.e. a click, an impression, a sale)
Cost Per Click (CPC) – an online ad model where the advertiser pays a pre-set amount whenever that ad is clicked
Cost Per Thousand (CPM) – the cost to reach 1,000 people via a specific advertising channel or medium (1000 viewers on TV, 1000 page views, etc); or cost per thousand impressions
Crowd-sourced – usually referring to content; when you let your customers, users or other 3rd party subject experts create quality content for you to share on your site or other social platforms under your brand or organizational name. Content may come from a contest, as part of testimonials, or guest posts. Always give credit fairly to all contributors, including social media handles. (see also User Generated Content)
Curation – collecting, organizing and sharing already published content (usually from a 3rd party) via a blog, social media or email newsletters.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – often refers to software designed to help you keep track of contacts, leads and customers at different phases of interaction with your organization; system holds all contact information, details of meetings, personal info (birthdays, anniversaries, hobbies, interests – anything to help you personalize your contact or products with potential customers). Some systems include social networking information and profiles. Examples include: Nimble, Insightly, Salesforce, Zoho, Infusionsoft, Act!, SugarCRM, Pipedrive, HubSpot CRM, Contactually, Nutshell
D Terms
Demographics – personal info about users or customers (usually collected, studied or used in marketing in the aggregate – i.e. not identifiable to a specific individual); e.g. age, gender, occupation, education level, zip code, number of people in household, marital status, group affiliations
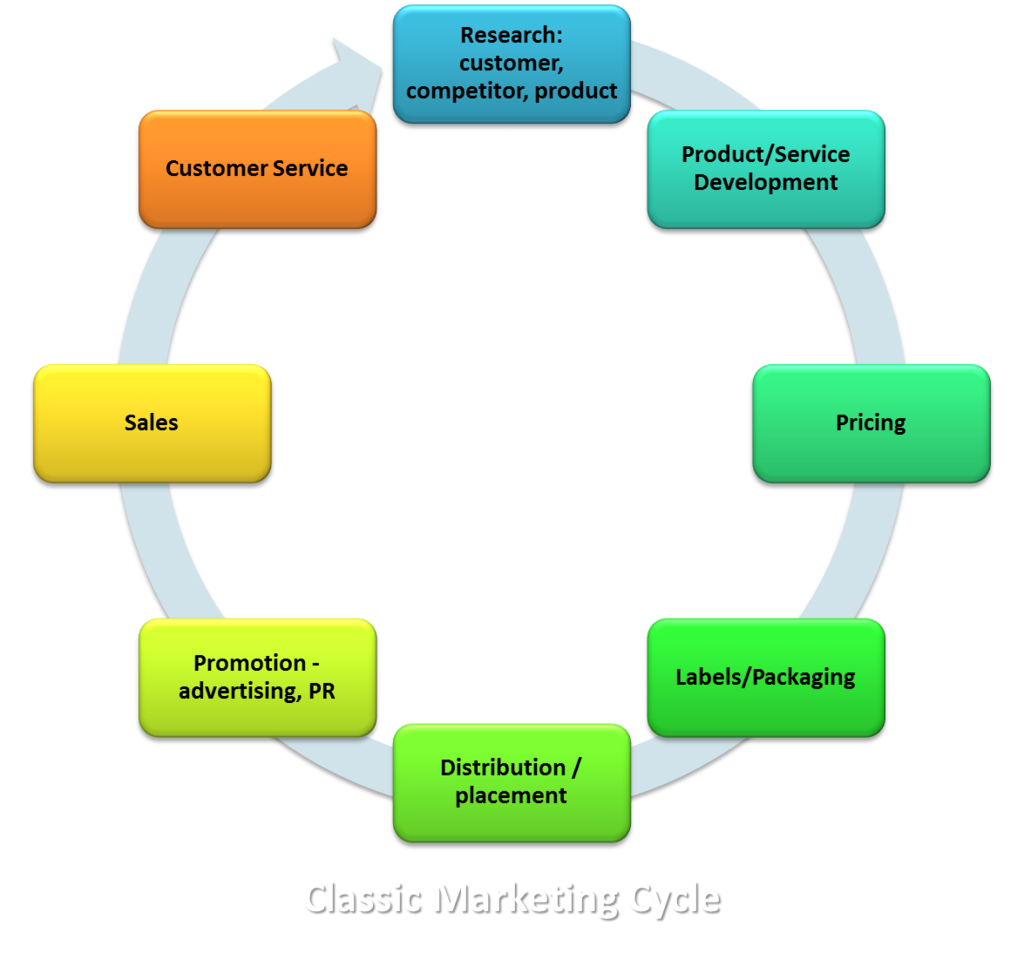
Distribution – how your products, goods, services or cause are delivered to your users or customers; also method your products or services are marketed, promoted circulated into hands of users; Channel of Distribution = network or system of resources, organizations that are connected to bring a good or service from beginning producer into hands of end consumer, completing a marketing cycle
DM (Direct Mail) – targeted advertising, fundraising or news delivered to prospects, customers, users or patrons via postal mail
E Terms
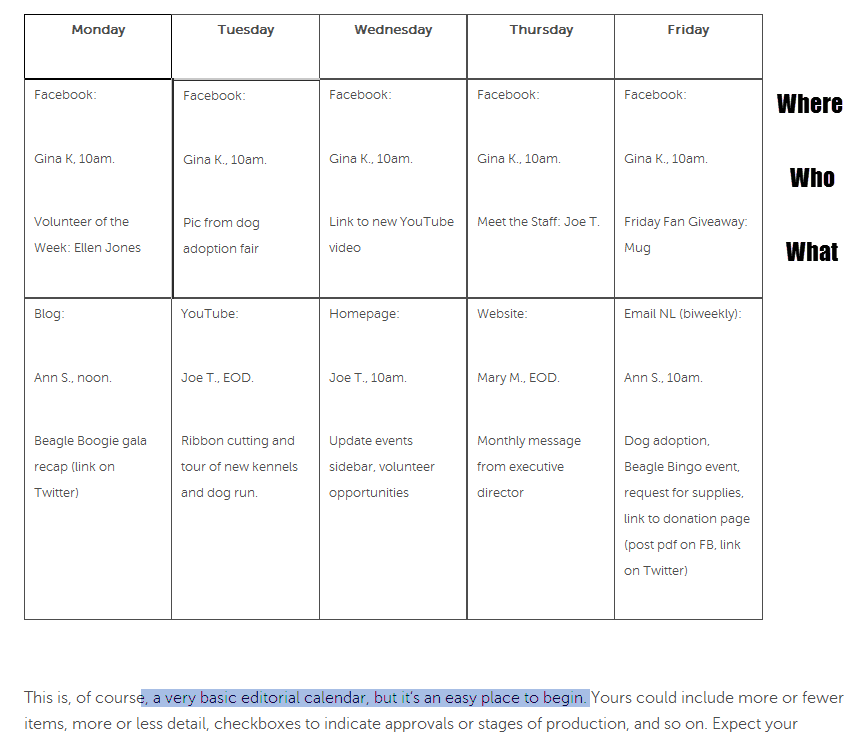
Editorial Calendar – a publishing schedule for your content that helps you organize, plan and coordinate what you are creating, publishing and sharing when and where. A calendar might include: timed themes for your content (April is Library Appreciation month; February will feature ‘best huddle with blanket and fireplace reads’, Wednesdays will be website tips; share archives or local history on#TBT, #Caturday, etc ); topics for blog posts; days you send emails, plans for each social media platform including links and promotions; what events you will promote on which channels, etc. You can keep it as simple as a Word doc or Excel chart, a team Google calendar, or use free and paid tools online. There are sample calendars online as well as tools to help plan and execute.
Email Marketing – targeted communication to users or customers for promotion or sharing of news about products, services or causes via email; email marketing is a more technologically savvy, cost effective and trackable form of direct mail marketing; true email marketing always involved wanted communications, not spam – users or customers have opted-in to receiving the message(s) [in compliance with the CAN-SPAM Act]
Engagement – or Engagement Rate – popular social media metric to describe or measure amount of interaction between accounts. Shares, RTs, ♥ or comments can indicate an interaction, a level beyond just reading your posts, Tweets or pictures.
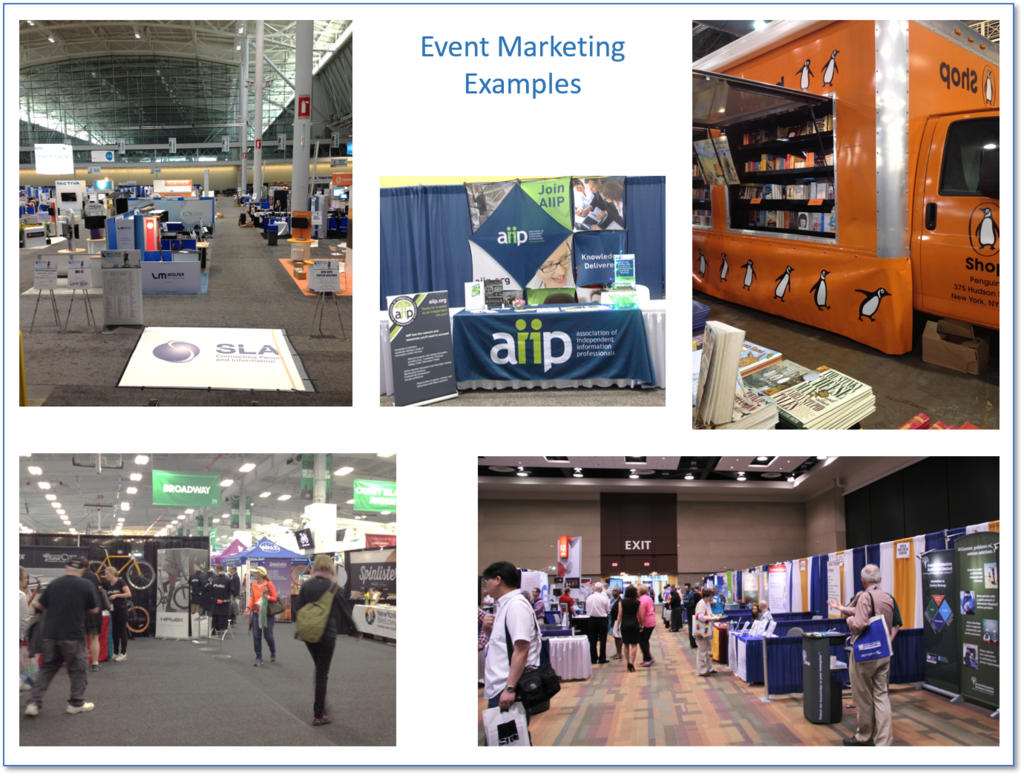
Event Marketing – promotional strategy linking an org or company to a specific event (festival, fair, sports event, competition, music event, trade show, conference); often includes sponsorship of some aspect of the event, but not always – having a booth or physical presence at an event is ‘event marketing’. This does not mean ‘how to market an event’ – that would be part of your overall plan or part of a promotion.
Evergreen Content – a gardening analogy to describe types of content – ‘Annuals’ are posts or content that is time-restricted or time-based, meant to bloom and last a short time; ‘Evergreen’ content gives good info and value no matter when a reader finds or sees that content, it is timeless and lasts and doesn’t have a season. Evergreen content tends to get higher search engine rankings for your site, higher traffic, and can be a page you refer to internally for some time. This is content that will help you for a long time after you publish it.
e.g. this page you’re reading with the glossary of key marketing terms is ‘Evergreen’ because most of these concepts will not change over time and it should stay useful even if you find it a year after I wrote it. Alternately, when I post about an upcoming workshop or a conference I just attended or give a trends report for a given year, that’s ‘annual’ or short-lived content.
e.g. Resource lists, lists of great curated content on a specific topic; FAQs; histories or timelines; how-to-guides on topics that don’t change frequently
F Terms
Focus Group(s) – a way to gather qualitative research about users or customers by gathering them in a group, physically or virtually, and asking guided questions or exercises; learn more about behaviors, values, beliefs, desires or reactions to concepts; in recruiting, often preferable to have multiple, varied, homogeneous groups to encourage free discussion and then compare results across groups; focus groups are small by nature and can gather more in-depth information than a questionnaire or other methods; data is not always representative across all users or customers, unless well-designed with variety of users or customers, or desired users/customers
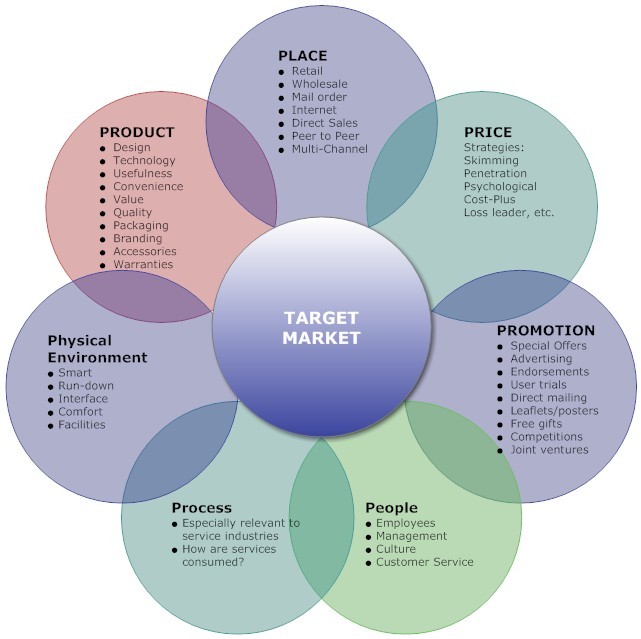
Four Ps (or the Seven Ps) – Product (or Service), Price, Place (i.e. distribution), Promotion
Product – the item/service that satisfies a customer/user demand and all its features and benefits
Price – what
The 7Ps of Marketing; the Marketing Mix components
customer/user exchanges for the product – setting or changing price is part of overall business and marketing strategy; for nonprofits this might include a membership fee, prices on items sold for fundraising, the time or resources given up in exchange for a service, the action requested by a cause, the other ‘costs’ for using a service or attending an event (e.g. hard to get transportation to the library or an event, so ‘cost’ too high to attend)
Place – how and where the user/customer gets the product; marketing via changes in Place might include adding a new location, increasing hours, adding a kiosk at seasonal location, taking services to community, live-streaming an in-person event or changing your website, adding a donation button online
Promotion – the methods (channels) of communication to a user/customer about the product and its price and place (i.e. tactics; advertising, public relations, sales, sales promotions, etc)
Some marketing experts and teachers have expanded this to more Ps and to cover services and service-based organizations: Physical evidence (that service was performed or delivered), People (the employees delivering the service and way they do so), Process (systems that affect delivering service)
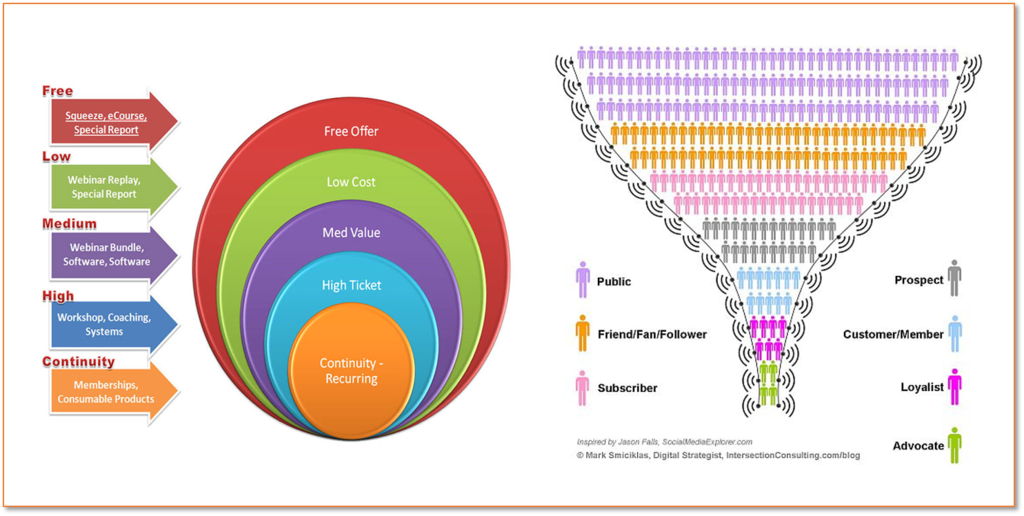
Funnel – the process or ‘journey’ of a prospective user/customer/donor through phases or levels of commitment, from a lack of awareness to greater awareness and trust, towards a purchase, donation or otherwise becoming a customer or user. The wide, top of the funnel is where someone has the least awareness of your organization or its services and the lowest level of commitment; the narrow, bottom of the funnel represents the smaller number of people who are aware of the org, become its fans and have made a greater commitment. Marketing actions are taken to bring people through the funnel, with the understanding that not everyone filters down to the bottom or tip. Different marketing strategies and tactics may be used at different stages of the funnel.
e.g. Top of Funnel = build awareness, educate; get people to follow you on social media or Like a post; Middle of the Funnel = more engagement, deeper connections and trust; encourage small (often non-cash) donations, sign-up for a newsletter, interact more on social media; Bottom of the Funnel = aware, engaged, believe in your mission and ready to take further steps to support you or use services; meaningful investment of time or money, volunteering, event registrations, monetary donations
Frequency – the number of times a person, household or other member of a target audience is exposed to media or paid ads over a specific time period; in paid advertising it’s considered necessary for a customer to be exposed to ad multiple times in a campaign for it to be considered effective, but there are also caps because too high a frequency is unhelpful
G Terms
Geotargeting – a way of detecting a website visitor’s location and using that info to serve targeted, location-specific messages, ads, coupons or content
e.g. Apple’s iBeacons giving info + CTA, ‘location aware’ connection to user’s mobile device; mobile advertisers using GPS in smartphones along with apps (e.g. MLB’s Ballpark app lets you ‘check-in’ when physically present at a stadium, verified by GPS, and be sent coupons for team-specific merchandise, or codes for food at that ballpark; an iBeacon attached to a statue outside library or museum tells who statue is of + directs inside for more info, check out books on subject of statue)
Goal – concrete, specific, short term measurement of desired achievement; what you are pursuing in order to meet an objective
- increase in-person attendance at story hours by 10% vs. same time year ago
- increase library card sign-up among 18-24yr olds by 20%
- increase summer reading participation by 20%
- increase circulation and use of materials by 10% among current library card holders and regular users
Guerilla Marketing – a marketing tactic or technique considered to be ‘unconventional’, usually a low cost initiative designed for maximum impact/results for minimum effort/resources.
H Terms
Headline – the attention-getting sentence at the top of a page (webpage or content piece) to draw a reader in and entice to read further. Important for all web pages, sales pages, blog posts, articles and even emails. Headlines often appear in a different font style and larger size, bolded or otherwise made to stand out.
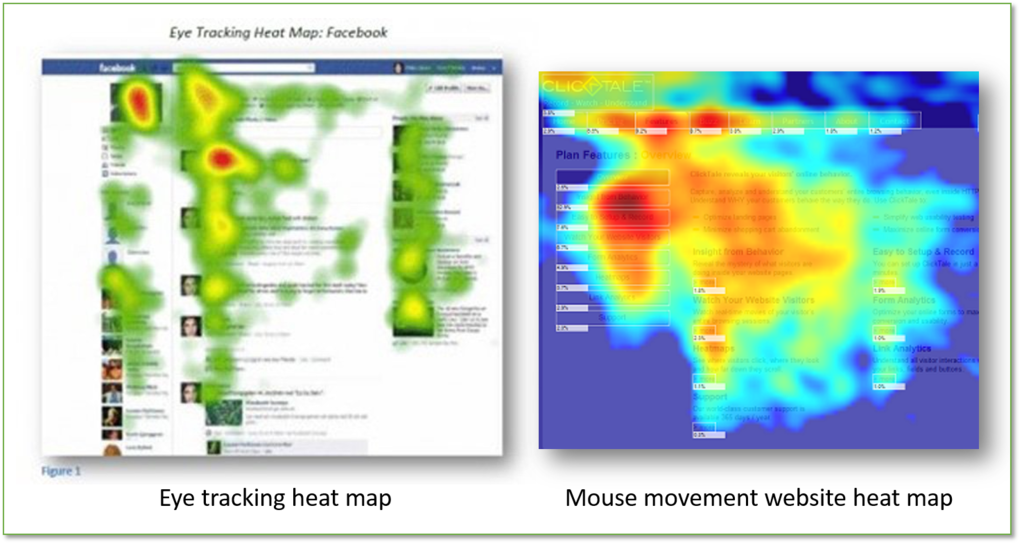
 Heat Map – a graphical representation (usually with shades of a color or warm-to-cool spectrum) to show varying degrees of a single measure; on websites, a heat map can show concentrations of clicks or eye-tracking
Heat Map – a graphical representation (usually with shades of a color or warm-to-cool spectrum) to show varying degrees of a single measure; on websites, a heat map can show concentrations of clicks or eye-tracking
I Terms
Impression – one instance of an online ad being ‘displayed’ (doesn’t guarantee it was seen)
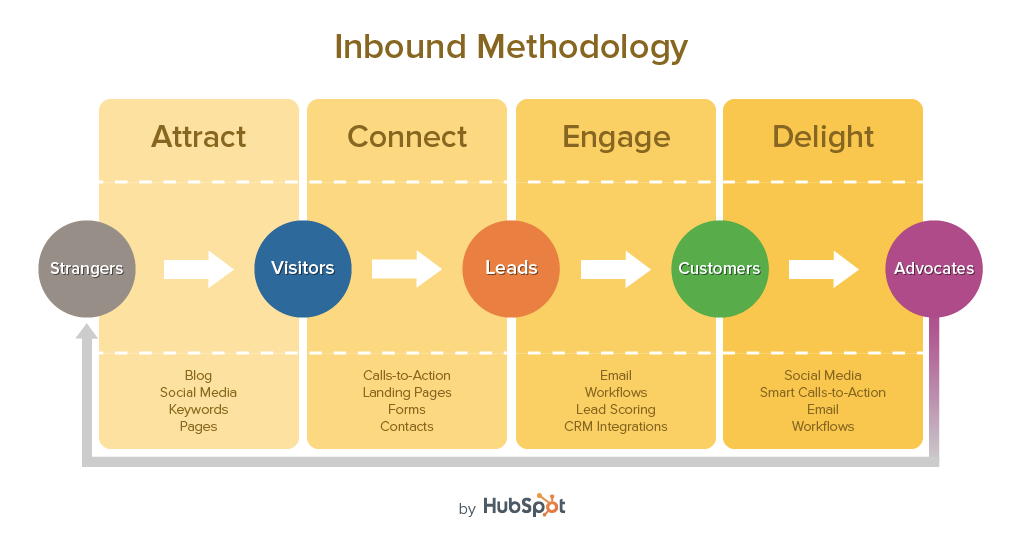
Inbound Marketing – often used interchangeably with ‘content marketing, but they are NOT exactly the same [Content Marketing is generally a type of Inbound Marketing]; Inbound draws visitors, potential customers, prospective patrons towards you, IN to your organization vs. ‘traditional’ or old-school advertising which pushes its message OUT. Inbound is about attracting visitors, being easily found online, having visitors come back to your site over and over, usually with high quality, helpful content.
HubSpot’s Inbound Marketing and Lead Nurturing Model – main stages = Awareness -> Evaluation -> Purchase
Outbound Marketing – marketing messages pushed outwards at masses of consumers, with little input from consumers on the actual message(s); ‘traditional’ TV, radio and magazine ads, cold-calling, ‘junk mail’, trade shows, billboards, purchased lists
Influencer – person whose views or platform can influence the attitudes and behavior of others, including making decisions, purchases or donations.
Infographic – visual content that uses graphs, icons, arrows or other elements to present statistics, a timeline or a story in a visual way.
Integrated Marketing – process/system/framework that emphasizes that planning and connecting all marketing elements is preferred; to ensure all the points of contact and communication between a brand and a consumer are coordinated and consistent over place and time (regardless of individual media channels).
Incentives – something offered to reward or motivate action by sellers, users, consumers, donors; bonuses, promotions, contests, competitions or games, give-backs, freebies, premiums, sales promotions, pass-along deal; can be coupons, discounts, prizes, money, virtual or physical items.
J Terms
Wait … how is that there’s no marketing term starting with J to explain? I should aim to have one named for me. 😉
Thanks to a suggestion from Michael Schofield of LibUX, let’s add a J-term that we should all be aware of … and NOT use in our marketing!
Jargon – that language, set of terms, acronyms, created words and more that are special and specific to a profession, niche, trade or group. Words that members of the group know and understand (or they come to know), but which are confusing to the ordinary public or non-members. These are often technical terms, industry-specific words, or words whose meaning is different for the ingroup vs. others. Libraries and librarianship have TONS of jargon terms – let’s be really careful about what we say or how we describe our products or services with words that don’t have the same meaning, weight, accessibility or understanding with our patrons and users.
K Terms
Keyword Phrase – a phrase that someone enters in a search engine to try and find something they’re looking for. Website creators and owner attempt to build pages to best rank for these phrases in search results by writing content that features a phrase and words related to that phrase.
L Terms
Landing Page – a single web page where one sends traffic with a goal of encouraging a single action; it doesn’t have additional navigation, links or ways for someone to easily leave without completing the desired action. Goal usually involves capturing a visitor’s information in exchange for offer of something of value for purpose of email marketing, follow-up contacts.
E.g. A webinar registration page, an email opt-in offering an ebook, a form to be contacted for an appointment, a page selling an ebook, a page for collecting registrations for a free event, a form to collect signatures for a petition, etc. Only 1 single goal per landing page.
Layout – the physical design or format of a physical piece of marketing material, showing the placement of artwork/images, header, headlines, subheads, body copy, contact info and any other graphical elements; particularly used to describe printed ads, pieces of direct mail, publications, and other physical collateral (brochures, flyers, business cards, post cards, bookmarks, folders).
Lead Magnet – an enticing, useful, educational, helpful piece of content or free resource offered to visitors in exchange for contact information (usually a name + email address); content is emailed or digitally delivered after completion of the form, and further follow-up takes place. (in the image above for Landing Page, you see I offer a free eBook on tools for library marketing if you join my email list on that page – the eBook my lead magnet, click hereto get it.)
Lifecycle – stages or phases to describe the evolution of the relationship between you and your audience, users or customers. There are various lifecycles discussed among marketers and marketing experts. E.g. the Product Lifecycle is a theory that all products and brands experience following sequence: Introduction, Growth, Maturity, Decline
Marketing Cycles –
e.g. John Jantsch’s hourglass marketing model with Know -> Like -> Trust, Try -> Buy -> Repeat -> Refer
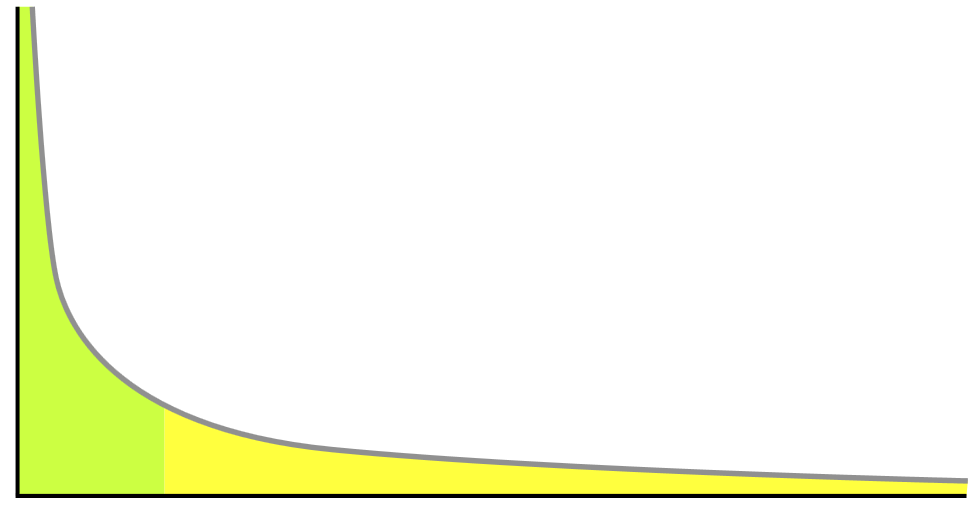
Longtail – a search phrase with three or more words, usually a key term and additional descriptors. They are more specific than a single or two-term search and if your content matches these longer phrases the visitor who follows that longtail search term to your site is more qualified and more interested in what your site offers. More and more searches online use longtail phrases, so it’s useful for your web pages and posts to use the same types of long phrases that your audience will search on.
Longtail graph
e.g. a shorter (and more competitive search phrase) = “Hawaiian cruise”; a longtail search = “single mom Hawaiian cruise”, or “single parents cruise Hawaii”
shorter = “organic coffee”, longtail = “organic coffee vs. regular coffee”, or “why pick organic coffee” or “is organic coffee better for you”
shorter = “summer reading selections”; longtail = “summer reading selections philadelphia schools”, “summer reading selections philadelphia library”, “what should my child read for summer reading”
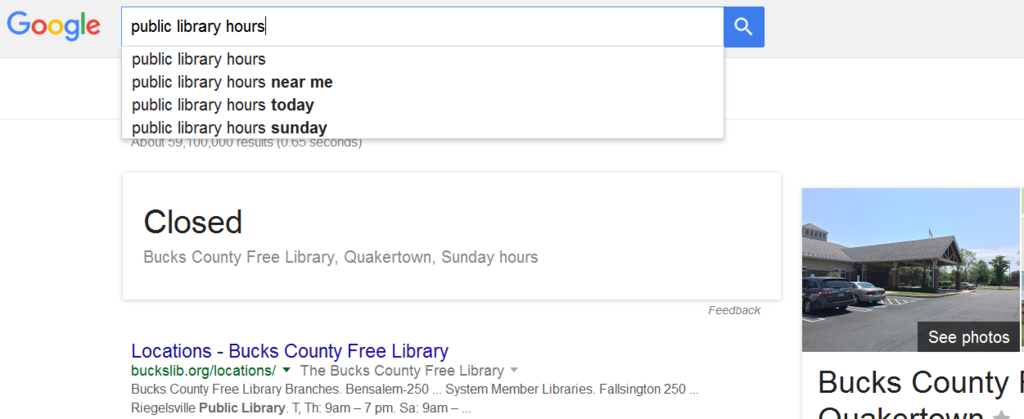
Example of longtail – Google Suggest offers even longer search phrases
M Terms
Marketing Mix – the mix of tactics, channels, variables that an org uses to achieve desired business and marketing goals; see the 4 (or 7) Ps model [the combo of price, product, promotion, place]; the mix includes what to budget to each variable, amount of time/resources, how to measure, and timing.
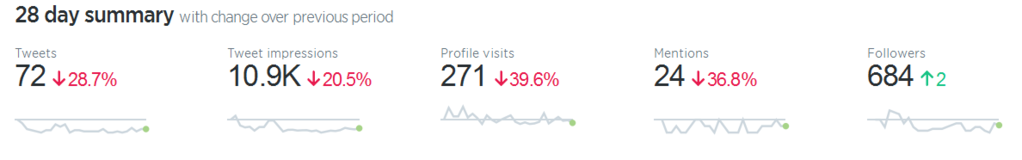
Metrics – a system or set of measurements to help quantify marketing elements or characteristics; e.g. SEO metrics to measure include: overall traffic, search engine traffic, conversions, top traffic-driving keywords, keyword rankings; e.g. social media metrics include impressions, engagement, reshares, followers.
Twitter Engagement Metrics
Mobile marketing – there are now more searches on mobile devices than desktops/laptops, responsive web design is key, your organization and site need to be easily found and seen on mobile devices – so it makes sense your marketing needs to work on mobile too. Mobile marketing refers to optimizing your messages, visuals, site, emails and more for viewing on mobile devices, being seen and sending promotions in time- and location-sensitive ways.
Multichannel – interacting with a customer via campaigns designed to appear simultaneously across multiple channels to promote goods or services; increasing the number of channels increases the odds that a brand or org will reach a consumer in their preferred method or channel; direct channels = org proactively reaches out to customer via a physical location, catalog, direct mail; indirect channels = websites, social media, email, text messaging, mobile marketing
N Terms
Newsjacking – piggy-backing on, or taking advantage of, a breaking news event or hot item/trend in a news cycle (overall or in your given industry, niche, field, local market) to insert your brand/organization into the news stream. Requires fast action and treading carefully to not negatively affect brand. See expert David Meerman Scott’s book Newsjacking.
Newsletter – either printed or online via email, a digest or collection of organizational news, tips or noteworthy info to share with a specific audience; newsletters can be free, paid, available to the public or to a limited membership/audience; generally a quicker production and distribution than a magazine, less formal than a newspaper, different from a blog post
Want to see an example?
Check out the archives for my marketing insights newsletter and my marketing round up emails.
Niche – specialization, segmentation or subset of an overall market or audience; a small, specific, well-defined portion of the total population; marketers create niches by using research to find the needs or wants that aren’t being addressed or met by other brands or orgs and developing a way to identify similar members of that niche and deliver their goods or services to them; ‘a big fish in a small pond’ strategy
NoFollow – a website and SEO related term; it tells SEs (search engines) NOT to count that link or pass on its ‘trust’ factors to the destination URL By not passing on ‘credit’ or ‘trust’ you can avoid associations with potentially spammy sites, sites with questionable content (but that you might still have a good reason to link to, or show as an example of something), or to not run afoul of certain webmaster guidelines.
e.g., for site owners that do not want to give full “follow” credit to links posted by users in their forums or blog comments; e.g. you need to show an example of a ‘what not to do’ and link goes to a questionable site, which you don’t want affecting your rankings or SEO
Nonprofit Marketing – marketing of a product, service, cause for which overall goal is not to make a monetary profit for the organization/marketer; may include promoting or selling goods or services to support organization, but profit is not primary; often includes same marketing mix, channels or tactics as for-profit marketers
O Terms
Objective – a desired result to achieve by a particular time; usually broader than a goal, an objective can be broken into several more specific goals; there are organizational and marketing objectives
Offer – in content marketing these do NOT have to mean things for sale, they can refer to high quality content that is ‘gated’ behind a password or requiring an email subscription entry in a form on a landing page. An offer might be for a checklist, worksheet, template, free webinar, ebook, free software, etc. It’s what you are ‘offering’ in exchange for something else (an email opt-in, small payment, trial).
Opener – the part of content or copy that comes after a headline. It should be compelling, engaging and entice the reader to keep moving down the page. Also known as an ‘introduction’ or ‘introductory paragraph’ [but is usually just 1-3 sentences].
Opt-in – when some material is restricted in access and requires the giving of contact info or a request to specifically receive the material; example, for email marketing someone must opt-in to the list/membership, showing they choose to receive your messages (CAN-SPAM compliance); See also, Lead Magnet, offering something to encourage someone to opt-in to receive an email newsletter (give an ebook, coupon, video, e-course, free event ticket)
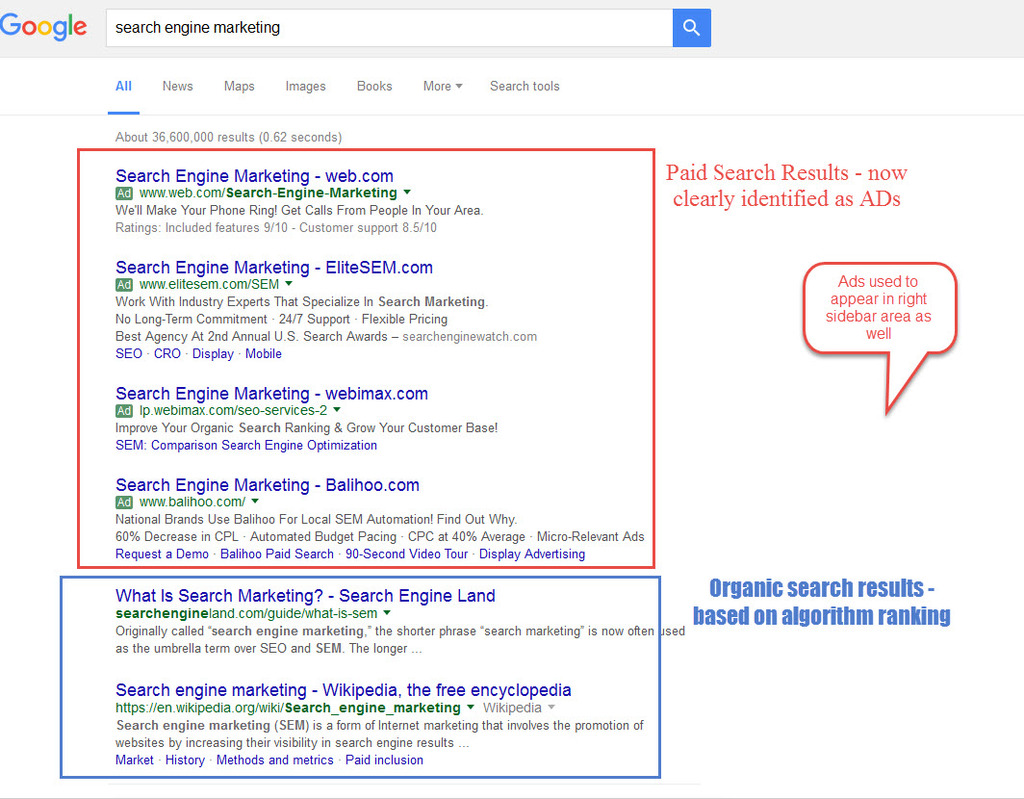
Organic Search Results – listings in search engine results that were not paid for (similarly, Organic Traffic is that which comes to a site through individual’s searching on their own, clicking a link that is not sponsored, a paid ad, etc); appear ‘organic’ or ‘natural’ because results show in listings only based on standard algorithm of the search engine and ‘natural’ process of crawling and indexing sites (not influenced by any payments)
P Terms
Personas – avatars or ‘people types’, a collection of demographics, psychographics and attributes to describe some subgroup, particularly of your target audience/marketing; e.g. the particular collection of gender, age, salary level, education, leisure activities, family status and other definable behaviors that make up your ideal customer; use to focus your messages to the correct audience, to help segment and select media channels.
Positioning – how you want your organization, brand or product to be perceived in the market relative to your competitors and alternative options in your key users/customers minds
Power Words – emotionally-charged words or phrases. Often used to set a scene, create a mental image, inspire, persuade or influence a reader. There are positive and negative power words- be careful not to overuse the negative ones. Example power words for marketing: agony, attention, eager, frantic, maximize, mind-blowing, survival, struggle, fooled, vulnerable, amazing, eye-opening, spectacular, delight, bargain, jackpot, proven, and guaranteed.
Promotion – can have several meanings in marketing; 1) in the classic 4 Ps model and marketing mix, promotion techniques include advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations as ways to achieve specific marketing goals; 2) a type of advertising or communication that offers a special price, sale, discount, temporary change in price, new season, limited-time availability of goods or services, new product/service debut – the key is that this is limited in duration and different from ‘every day’ communication about the org, brand, product or service
Psychographics – attributes based on consumer behaviors, values, lifestyles or interests, not personal info; orgs can (and should) segment a market or target based on lifestyles or psychographic information for better results
e.g. the company Orange Boy has been hired by many libraries to perform data analysis and segmentation using library and community data as well as psychographics to create user personas and influence marketing strategies and promotions. [I’ve attended multiple presentations and case studies of library marketing successes in partnership with OrangeBoy and they are a sponsor for the Library Marketing and Communications Conference, of which I am a part]
Q Terms
Uhoh. Missing another letter. Your chance to tell me a ‘Q’ library marketing term to define and illustrate for you!
R Terms
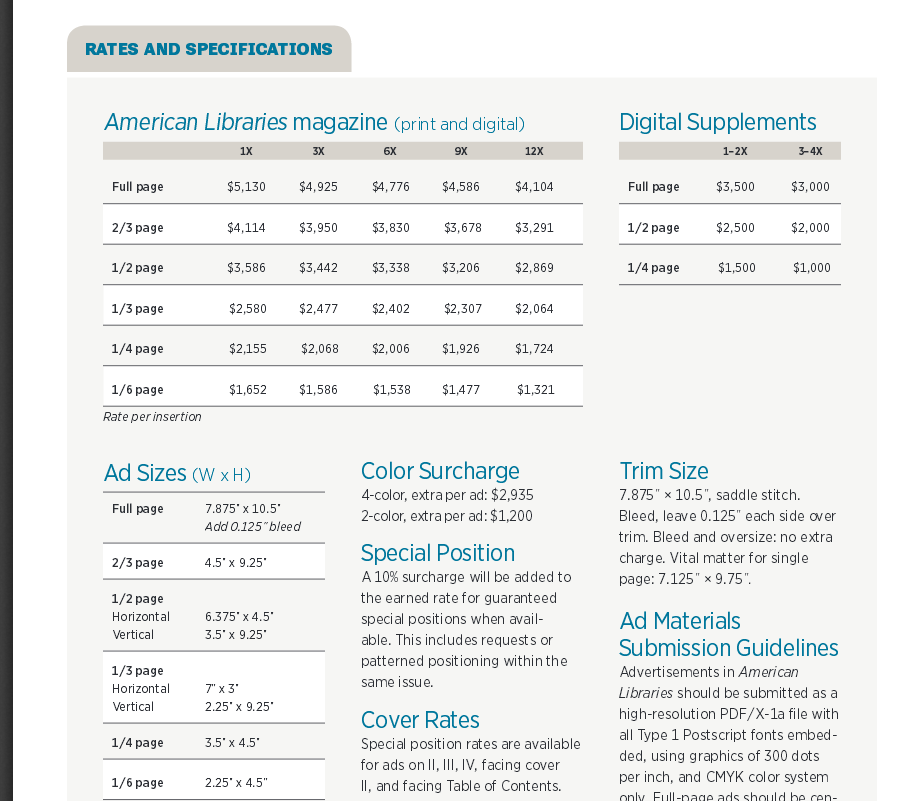
Rate card – document or information detailing the prices for paid ad placement options in a publication
Reach – the number of people or households exposed to a particular piece of paid advertising or media during a specific time period; reach is often given as a % of the total number of people in an audience, target market or geographic area
Relationship Marketing – marketing designed to develop, manage and maintain long-term, trust-built relationships with users/customers, suppliers, distributors and others in the marketing cycle; often makes use of automation, social media and tools like CRM software or loyalty programs; term often connected to author Mari Smith
Responsive web design – websites or website themes that automatically adjust to fit any device – from desktop to smartphone – and show content in way optimized for the device a visitor/viewer is using. The user experience should be seamless and not require adjustment from them to view/interact with content or navigation. Responsive web design has become a standard requirement. If you can’t use or create a responsive web design, you need to consider a separate mobile website or app so your users can optimally view and use your site on a variety of devices.
ROI (Return on Investment) – benefit to org from investing in a particular resource or action; a high ROI means you gain more than the action cost in terms of time, manpower, money; marketing ROI is often the contribution attributed to marketing divided by marketing costs or investment; e.g. if you invested $100 an you earned back $150 or its equivalent, your ROI is 50%.
S Terms
SEM (Search Engine Marketing) – paid search result placements or ads; sometimes refers to all search-marketing activities, paid and organic search efforts
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) – the idea of being able to ‘optimize content’ in order to gain more favorable placement in search results and ‘organic’ or natural traffic. At a basic level, it means making your content easy for a search engine to find and index – create useful content; appropriate titles, headlines and sub-heads; description tags; outgoing links. Search engine algorithms and ranking factors are always changing, there are lots of misconceptions, and there is NO way to guarantee result placement – but well-structured and described content can help.
Copyblogger has another 60second animated term definition +good explanation for SEO here.
 Segmentation – dividing an entire geographic, behavior, interest base or entire market into more specific, distinct subsets of potential customers/users/donors who are likely to have same interests, demographics, behaviors or needs; each segment might get its own marketing strategy or different plan and set of tactics or campaigns; segmentation reflects that not all users/customers/donors are alike and can’t be reached or engaged with exact same media or message; segmenting makes marketing more efficient and effective.
Segmentation – dividing an entire geographic, behavior, interest base or entire market into more specific, distinct subsets of potential customers/users/donors who are likely to have same interests, demographics, behaviors or needs; each segment might get its own marketing strategy or different plan and set of tactics or campaigns; segmentation reflects that not all users/customers/donors are alike and can’t be reached or engaged with exact same media or message; segmenting makes marketing more efficient and effective.
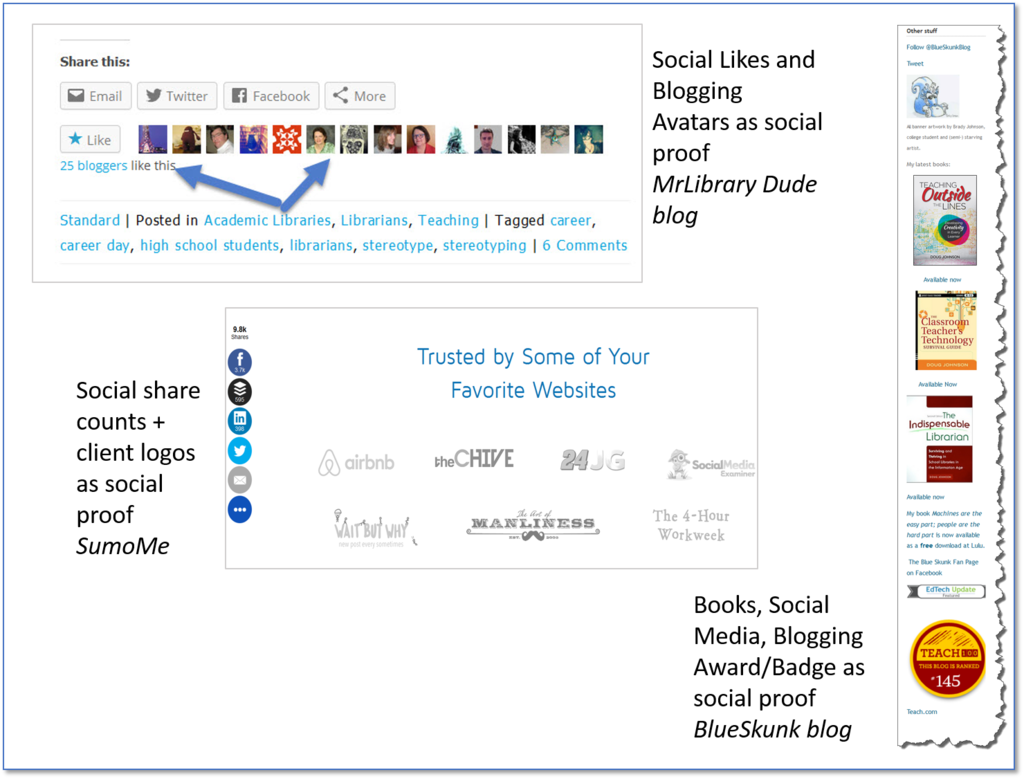
Social Proof – refers to the psychological phenomenon that people will take recommendations and advice from others on how to act or think in a situation, or what to do or buy. We are even likely to let the recommendations of strangers influence decisions over no recommendations. People tend to think, ‘if others are sharing something, it must be good’, or ‘if others are buying this item and it has lots of stars, it must be better.’
e.g. testimonials, quotes from other users or purchasers, case studies (even very short ones) with users/patrons, reviews (Amazon, GoodReads, Yelp), the number of likes/clicks/retweets a piece of content has, seeing the logo of news organizations or well-known blogs on someone else’s site, number of followers/fans someone has
SMM (Social Media Marketing) – tactics as part of an overall marketing strategy or plan that uses social media platforms to build interest, awareness of an organization or brand and to increase web traffic to the org’s site
Split Testing (A/B Testing) – a method of using online tools or platforms to conduct a controlled test over marketing variables – such as email subject lines, website headers, opt-in offers, landing pages, variations in copy, the color +/or text on a Call to Action button, ads, etc. Any time you pit two variations against each other and measure for clicks, completions, opt-ins, purchases or other desired action. Your base/original is the Control (A) and the version with slight variation is the Test (B). Don’t change too much between A and B or you won’t know what caused a difference in action.
Check out this podcast with definition and description from CopyBlogger and their Rainmaker program.
Strategy – the statement, plan or essential structure for how your organization aims to meet its marketing goals; strategy gives direction, purpose and helps make decisions on what tactics to use or not; strategy identifies the market, target audience, any subsegments, your brand positioning, your unique value statement, the specific goals and milestones to measure by, the specific marketing mix elements (or tactics) you will use and your budget (inc time and resources as well as money).
Style Guide(s) – a resource to document and standardize aspects of branding, communication, design and marketing by an org; style guides help when an org has multiple members involved in graphic design, content creation or creation of marketing materials to keep things consistent; it might include preferred abbreviations, spelling (is it ebook or e-book, “white paper” or “white-paper” or “whitepaper’), punctuation, or other grammar rules as well as how to use the logo, brand colors, brand fonts, image preferences, the corporate or organizational ‘vernacular’ or tone of voice; give visual examples of what to do, or not do [for examples of good style guides see this post]
Sub-head, sub headline – the smaller headlines through your content, dividing it into easier to read chunks or section. On a web page, these are often ‘header 2’, or ‘header 3’ or higher. Smaller font sizes and less emphasis than a headline, more than body text.
 Target Market (audience) – the individual (or group) with a set of attributes, demographics, psychographics who make up the intended viewers/recipients of a marketer’s messages. You can have more than one target, and each should receive their own customized set of messages – there is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Dividing one’s target market or audience into smaller, even more relevant sections is called “segmentation.”
Target Market (audience) – the individual (or group) with a set of attributes, demographics, psychographics who make up the intended viewers/recipients of a marketer’s messages. You can have more than one target, and each should receive their own customized set of messages – there is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Dividing one’s target market or audience into smaller, even more relevant sections is called “segmentation.”
T Terms
Taglines – also called a slogan, a brand line, catchphrase; a short set of memorable words or key phrase that sums up the main idea of your brand or a particular advertising campaign; really good taglines include a key benefit, help differentiate and give a positive feeling about the brand
You can probably guess the companies/brands from these famous taglines: “Just Do It”, “Think Different”, “Melt in your mouth, not in your hands”, “The uncola”, “Are you in good hands?”, “Don’t leave home without it”, “The ultimate driving machine”, “Like a rock”, “Because You’re Worth It”
Testimonial – written or video recommendation or referral from a happy, satisfied user/customer/donor; testimonials affirm the quality, value, customer service, performance of a product or service; powerful marketing tool because of the weight we give to evaluations from other customers and their experience
U Terms
Unique Visitor – web measurement/analytic term; the number of visitors to a site, each counted only once, who visit a site over a 30 minute period as measured by your stats/analytics software.
User Generated Content (UGC) – content created by your users, audience, fans and shared online (can be on your own site, system or platform or on a social platform, or shared to the library’s account on social media sites). UCG may be part of a promotion or contest, to offer personal experiences, for self-expression initiated by the users, to share or connect with other users. Make sure you work out ahead of time why you are collecting UGC and be sure to get permission and give credit to creators.
e.g. sharing photos of themselves with books, ‘shelfies’, YouTube videos, mashups, book reviews, memes, Wikis; community members guest-posting to a library blog; library Instagram account sharing a collage of pics every month tagged for library; ChiliFresh.com – interactive community-led conversations hooked to catalogs; social discovery in catalog ; LibraryThing for Libraries and user tags
V Terms
Video Marketing – incorporating video-based promotional content for a product or service into your marketing plans; videos of various types are created and uploaded online for sharing; videos for marketing are usually short, 2-5min or less and make use of popular video sharing sites and visual storytelling; videos are uploaded to 3rd party video sites to take advantage of their large traffic and search capabilities as well as ease of social sharing; don’t overlook hosting the videos on your own organizational site as well
e.g. user testimonials, demonstrations of products, screen-captures of online tools or software in action, animations, video of events, how-to videos, explainer videos, videos of staff, case study videos, behind-the-scenes videos
V/O (voiceover) – the voice of a person reading a script over a radio or TV ad, or over presentation slides turned into a video, or voice narrating or reading script while footage shows in a film or video
W Terms
Webinar – a learning or training experience conducted using web-based software and often with visuals, presentations, videos and audience interaction components. Some webinars show the speaker in addition to slides or visuals, some allow audience to be seen as well, some have forms of audience interaction. Often used for teaching, training, panel presentations or presenting new products or services in a demonstration. Can be offered free or paid as a form of marketing and lead generation, a premium offering to membership, or way to reach a wider audience.
White Paper – shorter than an e-book; well-written, researched paper, guide or report to address a problem and present solutions – often with the writer/organization’s product or service featured as one of those solutions. May also present recent research and statistics in text and graphical form. Often seen in a business-to-business (B2B) marketing or sales scenario – as white papers can be technical, serious and slightly academic in tone.
Widget – web term, a small piece of software built into site or interface to give additional, discrete function, personalization or added content, particularly in sidebars or footers of content management systems like WordPress, Drupal, etc.; e.g. displays latest tweets, shows local weather, add an RSS feed
Word of Mouth (WOM) – the act of sharing news, communications, recommendations or referrals of a product or service by informal oral or written communication, from a satisfied customer/client/user to a prospective user/customer of that brand/good/service.

“Sharing is caring!” and good Word of Mouth marketing
X Terms
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) Sitemap – website term for file with all the URLs on your site, like a map that helps search engines to crawl your site more intelligently. There are plugins that can help create an XML sitemap.
Y Terms
You – as in marketing messages need to say ‘you’ and talk directly to your audience, your users, your patrons. The message needs to be about them.
Z Terms
Zero Cost Strategy – a decision or tactic that doesn’t have any $$ costs or expenses when you execute it; many guerilla marketing tactics are ‘zero cost’;
e.g. you can improve perception and prospect of selling a home if you declutter the main rooms by packing excess stuff into boxes and putting the boxes in the garage or basement ; e.g. cross-promotion – you reach out to a local business that also serves mom + dads of early readers and offer to put their brochures at the front desk of your library or near storytime space, and they agree to post flyers, schedule of storytime hours and mention to their clients

Want More?! More Marketing Terms, Insights + Tools …
I send regular email newsletters with educational marketing insights and notes, cool tools and tips to use in your library marketing and communications work. I sometimes send roundups of my favorite blog posts or articles found and read that month. And you get notice of eBooks, videos, courses and workshops. Click below to subscribe and get a free eBook with more than 35 tools and tips for your library marketing toolkit.
Need to Learn More Marketing Terms in Your Library Work?
Additional Resources and Marketing Terms Glossaries:
CopyBlogger Glossary – http://www.copyblogger.com/master-content-marketing-concepts/ and http://www.copyblogger.com/content-marketing-glossary/
Jeff Bullas – 149 Marketing Acronyms http://www.jeffbullas.com/2016/04/19/149-marketing-acronyms-every-online-marketer-needs-know/
Brafton Marketing Glossary – http://www.brafton.com/glossary/
HubSpot Ultimate Dictionary of Marketing Terms – http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/inbound-marketing-glossary-list#sm.00017h8daigjtdfrzk929qsn2845u
American Marketing Association – Marketing Dictionary https://www.ama.org/resources/Pages/Marketing-Dictionary.aspx
Spokal A to Z of Online Marketing Terms – http://www.getspokal.com/the-complete-a-z-guide-to-online-marketing-terms/
Act-On – 63 Digital Advertising Terms https://www.act-on.com/blog/2015/08/63-digital-advertising-terms-every-marketer-should-know/